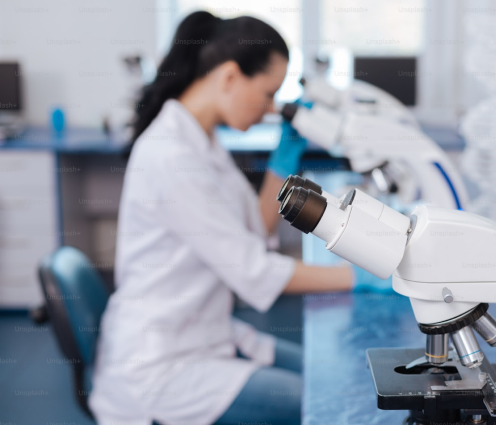
Bioinformatics and biotechnology are scientific fields related to biology and technology. Both areas play crucial roles in understanding biological processes and solving medical and environmental issues. This blog will explore the key differences between these two fields to help you determine which area is the right choice for you.
What is Biotechnology?.
Biotechnology is a branch of science that involves using living organisms, cells and biological systems to develop products and technologies that improve human life.
There are a wide range of applications for biotechnology; for example, medical biotechnology focuses on developing drugs, vaccines and diagnostic tools, whereas agricultural biotechnology focuses on improving crop yields, pest resistance and nutritional value through genetic modification.
What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics combines biology, computer science and information technology to analyse and interpret complex biological data. This is done with the goal of understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms of diseases and biological processes.
Like biotechnology, bioinformatics has a range applications. For example, bioinformatics tools are used to identify genetic mutations in tumours, aiding in the development of targeted therapies and diagnostic markers. Bioinformatics also helps to predict the interactions between drugs and biological molecules, which in turn accelerates the drug development process.
Key Differences Between Biotechnology and Bioinformatics
Methodology
The first key difference between biotechnology and bioinformatics is that biotechnology is primarily experimental and laboratory-based, whereas bioinformatics is computational and data-driven.
Bioinformatics focuses on creating and using computational tools to collect and analyse data. Biotechnologists then uses this data for lab experiments and other practical applications.
Tools
Biotechnology utilises tools like PCR (polymerase chain reaction), CRISPR (gene editing) and cell culture. Bioinformatics uses tools like sequence alignment and statistical analysis software and molecular modelling programmes.
Applications
Biotechnology directly creates products and technologies, whereas bioinformatics focuses on providing insights and predictions.
**
Bioinformatics specialists collect the data that biotechnologists need to carry out their work, so you truly cannot have one without the other.
If you enjoy laboratory work and hands-on experimentation with tangible outcomes, biotechnology may be the right fit for you. If you prefer working with data and computer tools, a career in bioinformatics may be a better choice.
Whatever you choice, both fields promise an exciting and impactful career, contributing to advancements that can change people’s lives and the future of the world.
Looking for a New Role – or Searching for Top Talent? Let’s Talk
Whether you're exploring your next career move or looking to hire skilled professionals, HRS is here to help.
We connect ambitious individuals with exciting opportunities across science, technology, and innovation-led sectors. From early careers to executive search, our expert recruiters work closely with both candidates and employers to ensure the perfect match.
If you're hiring, we’ll help you find the right people. If you’re job hunting, we’ll help you take the next step. Browse our latest jobs or get in touch to find out how we can support you.

